FREE: 10 Must-Know Tomato Growing Tips Get The Guide
Read our affiliate disclosure here.
The 6 Tomato Growing Stages Explained
Since 2010, Tomato Dirt has garnered 4.8+ million views, making it the web’s leading online source for growing tomatoes in the home garden. Award-winning writer and Tomato Dirt owner Kathy Widenhouse has helped thousands of home gardeners grow healthier tomatoes. Be one of them when you get Tomato Dirt’s Growing Guide here.
Posted 7.10.25
Before your tomato plants produce all that gorgeous fruit, they must go through 6 tomato growing stages. You can help them be their healthiest when you understand each stage and what your plant needs to thrive.
How can you know if your tomato plants are on track? First, the short answer.
How long does it take tomatoes to grow from seed?
It takes anywhere from 60 to 100 days after transplanting for tomatoes to mature and produce ripe fruit.
The exact length of time varies depending on your growing conditions and the tomato variety. Short season varieties take 85 days or less while long season heat lovers take 100 days or more.
Now, the long answer.
The 6 tomato growing stages
You can understand that process better by taking a close look at the different tomato plant growth stages: germination, seedling, vegetative growth, flowering, fruit formation, and ripening. If you purchase tomato seedlings rather than growing them for seed, then you will start to monitor your plants beginning at Stage 3.
Here’s the breakdown.
Tomato growth stage #1: Germination (5-10 days)
- What happens: In this initial stage, your tomato seed starts to sprout, and the embryonic root (radicle) emerges.
- Timeframe: 5–10 days after planting, if kept in a warm environment (70–80°F / 21–27°C). Cooler temperatures may delay germination.
- What to look for: Seeds swell, crack open, and a tiny root (radicle) emerges. Cotyledons (seed leaves) appear and push above the soil.
- What to do: Warmth, moisture, and oxygen are essential for germination. Keep soil moist but not soggy. Ideal temperature is 75–85°F / 24–29°C. Use a heat mat if needed to maintain temperature. Provide gentle light once the seedlings emerge.
- Watch for: Mold or damping off. Use sterile seed-starting mix and avoid overwatering).
Tomato growth stage #2: Seedling (2-3 weeks)
- What happens: After germination, the seedling develops a stronger root system and begins to resemble the typical tomato plant leaf shape. Its first true leaves emerge after the initial cotyledons (seed leaves).
- Timeframe: 2–3 weeks after germination. During this stage, the plant is still fragile and requires consistent moisture, warmth, and light.
- What to look for: True leaves appear after the cotyledons. Healthy plants are 2–4 inches tall with sturdy stems.
- What to do: Provide 14–16 hours of light daily. Gently brush or fan plants to strengthen stems. Water when top inch of soil dries out and begin feeding diluted fertilizer after true leaves develop.
- Watch for: If your seedlings are leggy, they likely lack enough light. Keep grow lights on for longer. If the leaves appear purplish, the seedlings have a phosphorus deficiency or temperatures are too cold. Adjust your liquid fertilizer accordingly and make sure your growing area is consistently kept at 75–85°F / 24–29°C.
Tomato growth stage #3: Vegetative growth (4-6 weeks)
- What happens: Your plant focuses on growing foliage, roots, and vines fast. It’s got an agenda – produce flowers and fruit as soon as possible so as to perpetuate itself. That’s why you’ll start to see buds and flowers during Stage 3, too.
- Timeframe: 4–6 weeks, depending on sunlight, nutrients, and spacing. If you started your tomato plants indoors, now is the time to harden them off and transplant them into the garden.
- What to look for: Rapid leaf and stem development. Roots will begin filling the container or garden space, even if you can’t see them. Your plant’s central stem will thicken and add plenty of branches.
- What to do: Transplant seedlings outdoors when nighttime temps stay above 50°F (10°C). Stake, cage, or trellis plants early so their developing root systems are not damaged later on by stakes. Begin your fertilizing routine with balanced fertilizer (such as10-10-10, fish emulsion, or a tomato-specific product) to help your plant grow strong. Begin pruning suckers so your plant concentrates on putting out buds.
- Watch for: Yellowing leaves can indicate a nutrient deficiency, best nipped early with by feeding plants regularly. Keep an eye out for early blight and consider beginning your preventative copper fungicide spray measures early. And look for pests like hornworm (that love tomato seedlings) as well as early like aphids, flea beetles, or whiteflies.
Tomato growth stage #4: Flowering (2-4 weeks)
- What happens: Yellow flowers appear on your plants – crucial for pollination, which leads to fruit formation. The flowering stage can last for 2-4 weeks.
- Timeframe: The flowering stage begins 5–7 weeks after transplanting. From your plant’s first bud to its full bloom can take 1–3 weeks – and can last until the end of the season for indeterminates.
- What to look for: Yellow flowers at stem tips or leaf axils. Pollinators in your garden are a good sign.
- What to do: Ensure your plants have adequate phosphorus (use bloom booster if needed). To maximize pollination, gently shake plants at the blossom tips. Water consistently to help plants avoid stress during flowering. If they’re thirsty, your tomato plants will pour their energy into their leaves so the plant can simply survive, rather than producing flowers.
- Watch for: Blossom drop – often an indicator of heat, drought, or lack of pollination. And keep an eye out for early signs of spots and curls on leaves.
Tomato growth stage #5: Fruit development (3-4 weeks)
- What happens: Flowers are pollinated, and small green tomatoes begin to grow.
- Timeframe: Fruit takes about 3–4 weeks to grow to full size after pollination.
- What to look for: Small green tomatoes forming behind flower bases. Fruits gradually increase in size until they start to ripen.
- What to do: Continue fertilizing with a low-nitrogen, high-potassium blend. Potassium aids in fruiting. (Nitrogen helps plants produce more leaves, which is not your goal during this stage). Mulch and water evenly to prevent blossom end rot. Thin or prune lower leaves if needed to increase airflow.
- Watch for: Blossom end rot -- dark, sunken spots on the bottom of fruits – which indicate inconsistent watering or plant stress. And slip shod watering can also lead to tomato cracking.
Tomato growth stage #6: Ripening (15-20 days)
- What happens: In this final tomato plant growing stage, fruit changes color and becomes mature and edible. Green tomatoes turn red, yellow, orange, or other colors depending on the variety.
- Timeframe: The ripening process usually takes 1-3 weeks (15-20 days). Some varieties, like cherry tomatoes, ripen faster; beefsteaks take longer.
- What to look for: Tomatoes change from green to their mature color (red, yellow, pink, orange). Fruits feel slightly soft to the touch when ripe.
- What to do: Pick ripe fruit regularly to encourage more production. When a tomato has been harvested from its plant, then the plant doesn’t need to sustain that fruit any longer. It has more energy to devote to additional blossoms and fruit. Shade fruit from sunscald. Reduce watering slightly to concentrate flavor near harvest.
- Watch for: Overripe or splitting tomatoes. Keep an eye out for pests who steal and eat ripe fruit.
Summary of the tomato plant growth stages
From seed to harvest: 60–120 days
From transplanting to harvest: 60–85 days
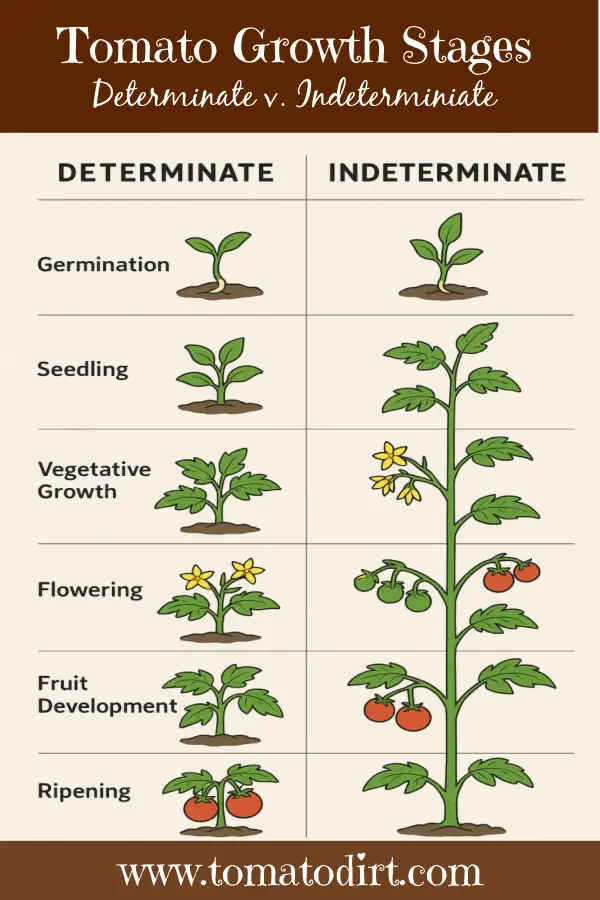
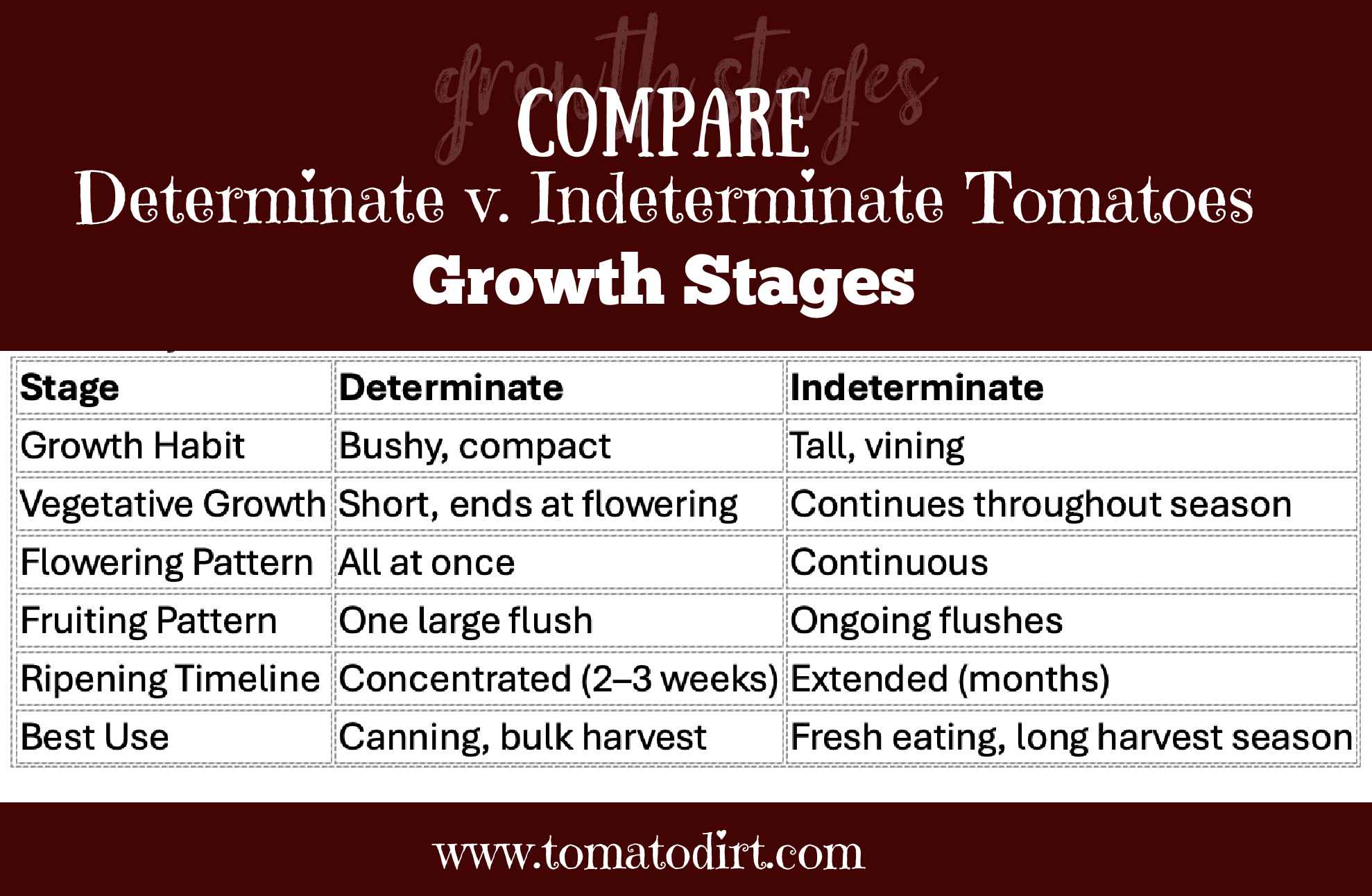
Tomato growing stages for determinates vs. indeterminates
The tomato growing stages for determinate and indeterminate tomato plants are fundamentally the same — germination, seedling, vegetative growth, flowering, fruit development, and ripening.
However, they differ in timing, growth habit, and fruiting patterns at certain stages. Here’s a breakdown of how the stages differ between determinate and indeterminate tomatoes.
Stages #1 and 2: Germination and Seedling
- No key differences. Both determinate and indeterminate tomatoes start life the same way.
Stage #3: Vegetative growth
- Determinate tomatoes grow to a compact, bushy size, then stop growing taller once flowers form. These plants focus their energy on fruit production early. Their vegetative phase is shorter than indeterminates – often just 4-5 weeks after transplanting.
- Indeterminate tomatoes grow tall and continuously throughout the season. They require ongoing support with stakes, cages, or trellises. Their vegetative period is longer, often extending while fruiting and ripening.
Stage #4: Flowering
- Determinate tomato blossoms appear at the ends of branches, all about the same time. They halt the plant’s vertical growth.
- Indeterminate tomato blossoms grow along the sides of the stem, allowing continuous growth. They bud progressively, often over weeks or months.
Stage #5: Fruit development
- Determinate tomatoes set fruit all at once, within a 2–3-week window. Their large harvests are ideal for canning, freezing, and drying.
- Indeterminate tomatoes develop continuously and keep producing all season until frost.
6. Ripening
- Determinate tomatoes have a shorter harvest window, since fruit ripens in a concentrated period – usually within a few weeks.
- Indeterminate tomatoes ripen gradually and continuously until the last frost.
Tomato growing stages are not fixed
The stages of growing tomato from seed to fruit are fluid and can blend into each other. Your earliest tomatoes will ripen on the vine (stage 6) while the plant continues to flower and produce fruit.
That spells an extended harvest for you.
More Tips for Growing Tomatoes
How to Increase Flowering in Tomatoes ...
How To Make Tomato Plants Grow Faster ...
Use This 6-Step Checklist for Tomato Plant Care ...
10 companion plants that protect tomatoes from pests ....
How
to control weeds in the tomato garden ...
10 Tips for Growing Tomatoes in Hot Weather ...
How Do You Ripen Tomatoes on the Vine Faster?
Is It Ripe? When To Pick Tomatoes ...
Get more tips on our Tomato Growing Tips Pinterest board...
Return from The 6 Tomato Growing Stages to Tomato Dirt home
As an Amazon Associate and Rakuten Advertising affiliate I earn from qualifying purchases.
SHARE THIS PAGE:
FREE! 10 Must-Know Tomato Growing Tips: 20-page guide
Get yours here:




Burpee Garden Tools- Stainless Steel Scoop

Deluxe Soil Text Kit for Home Gardeners